Dicranum Shennongjiaense, a New Bryophyte Species, Discovered in Shennongjia National Park
Updated:2024-07-12 Source:苟苟营?苔藓之恋

Chinese scientists recently discovered a new species of Dicranum in the Shennongjia Nature Reserve, which is named Dicranum shennongjiaense. This species exhibits unique morphological features, such as sickle-shaped leaves and strongly raised upper corner cells on the dorsal side of the upper leaves. This discovery enhances our understanding of Dicranum diversity and provides a new scientific basis for biodiversity conservation in the Shennongjia region.

1. Dicranum: An Example of Bryophyte Diversity
Dicranum (Dicranum Hedw.) is one of the most diverse genera in the Dicranaceae family, with more than 90 known species worldwide. Dicranum is widely distributed in Arctic alpine regions, peat bogs, and other cold and Arctic ecosystems. Dicranum exhibits rich morphological diversity, with significant variation in leaf, stem, and sporophyte characteristics, making its classification and identification challenging.
2. Discovery and Characteristics of Dicranum Shennongjiaense
Chinese scientists discovered a morphologically unique Dicranum species during a bryophyte survey in the Shennongjia Nature Reserve. Morphological and molecular phylogenetic analyses confirmed it as a new species named Dicranum shennongjiaense.
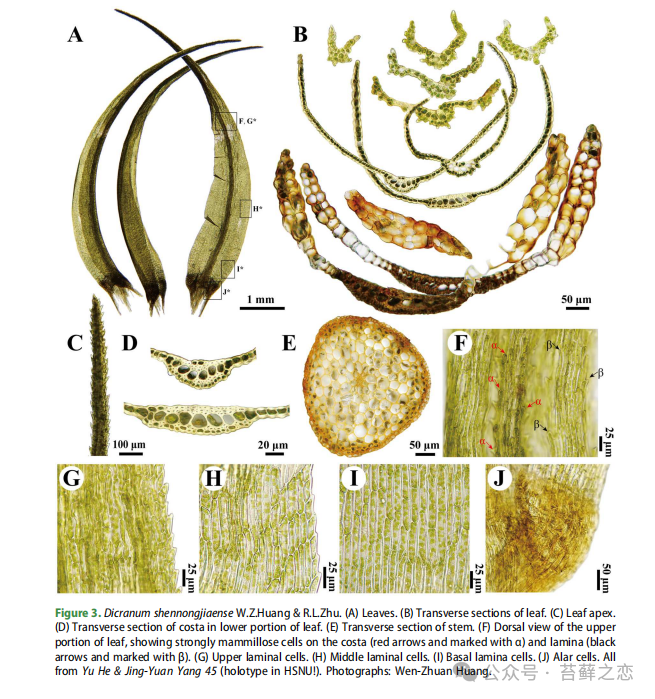
Key morphological characteristics of Dicranum shennongjiaense include:
Sickle-shaped leaves: The leaves are sickle-shaped or strongly sickle-shaped, with little change in shape when dry, measuring about 7-8 millimeters in length.
Leaf cell structure: The leaf cell structure is complex. The epidermal cells of the upper leaves have strongly protruding upper corner cells, with some cells having protrusions of 5-10 micrometers. Middle leaf cells are rectangular, measuring about 53-96 micrometers in length and 8-15 micrometers in width. Basal leaf cells are long-rectangular, measuring about 80-120 micrometers in length and 9-16 micrometers in width.
Leaf margins: The lower half of the leaf margin is entire, while the upper half has coarse serrations, with serration heights reaching 1-2 micrometers.
Leaf vein: The veins on the dorsal side of the upper part of the leaf have sharp serrations with an inter-serration distance of about 10-20 micrometers. They consist of only one layer of conductive cells, whose width is about 100-170 micrometers.
Auricle: The auricles are distinct, with 2-4 layers, brown in color, not extending to the leaf vein, and about 100-200 micrometers in width.
3. Significance of Dicranum Shennongjiaense Discovery
The discovery of Dicranum shennongjiaense holds significant scientific value:
Enriching Dicranum diversity: The discovery of Dicranum shennongjiaense increases the number of known Dicranum species, further enriching our understanding of bryophyte diversity. Currently, 36 Dicranum species have been found in China, with the discovery of Dicranum shennongjiaense bringing the total to 37.
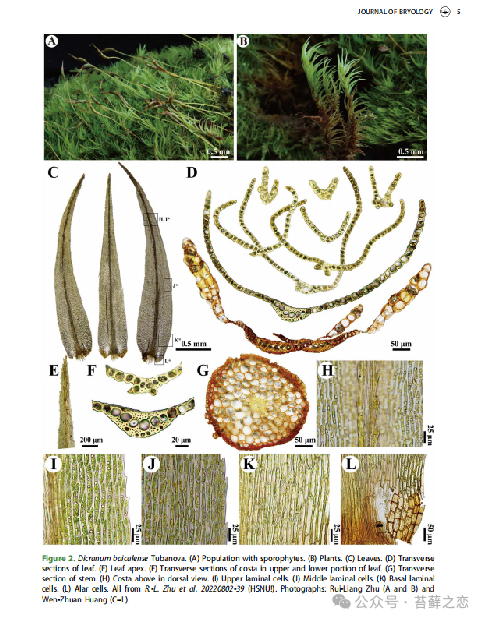
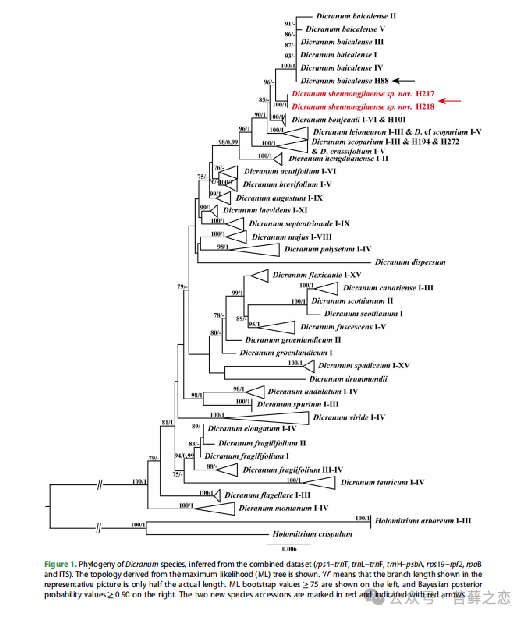
Revealing evolutionary patterns: Molecular phylogenetic studies of Dicranum shennongjiaense can reveal the evolutionary patterns and speciation mechanisms of the Dicranum genus. Research shows that Dicranum shennongjiaense is closely related to Dicranum baicalense from Russia's Lake Baikal region, but they differ significantly in leaf cell structure and leaf vein morphology, suggesting that Dicranum shennongjiaense may have developed unique morphological features through long-term evolution.
Providing a new basis for biodiversity conservation: The discovery of Dicranum shennongjiaense highlights the rich biodiversity of the Shennongjia Nature Reserve, providing a new scientific basis for biodiversity conservation in the area. As a UNESCO World Natural Heritage site, Shennongjia boasts a unique geographical environment and abundant biological resources. Protecting rare species like Dicranum shennongjiaense is crucial for maintaining regional ecological balance and biodiversity.
4. Protection of Dicranum shennongjiaense
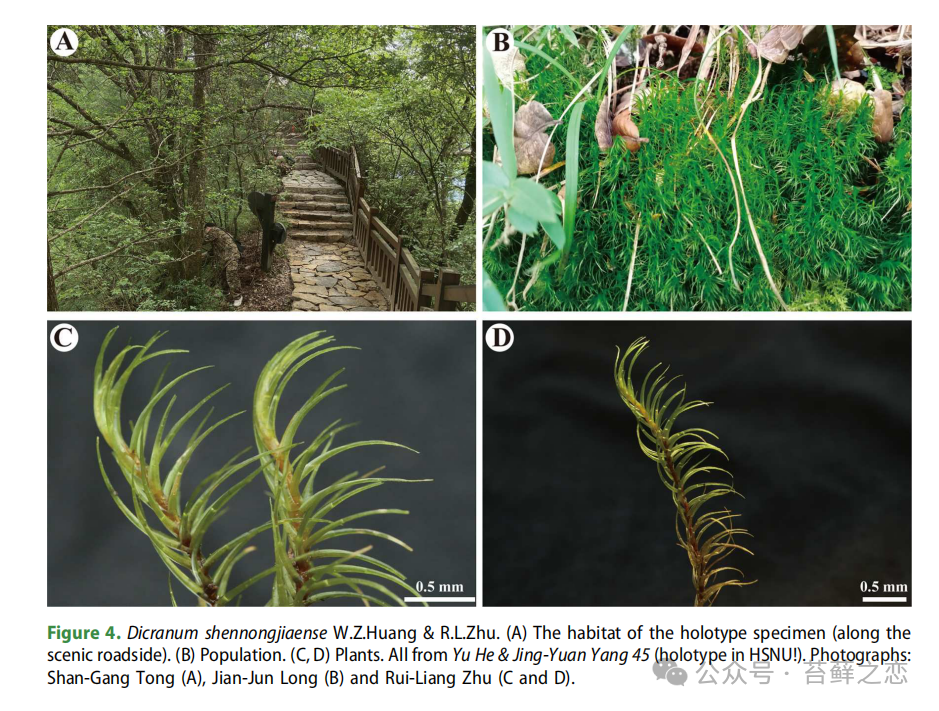
Dicranum shennongjiaense has so far only been found in the Shennongjia Nature Reserve and has a limited distribution range. To protect this new species, the following measures are needed:
Strengthen monitoring: The distribution range, population size, and growth status of Dicranum shennongjiaense should be regularly monitored to track its population dynamics. For example, GPS technology can be used to record its distribution points, and field surveys can be conducted to monitor its growth and population changes.
Protect habitat: The growth environment of Dicranum shennongjiaense should be protected against human activities that could damage its habitat. For instance, tourist access to its distribution areas should be restricted to prevent trampling and picking, and forest fire prevention and pest control efforts should be enhanced.
Promote science education: Public awareness about Dicranum shennongjiaense and the importance of bryophytes and biodiversity conservation should be raised. For example, educational materials should be created and outreach conducted in the Shennongjia Nature Reserve to educate the public about the significance of bryophytes and encourage public participation in biodiversity conservation.

The discovery of Dicranum shennongjiaense is a significant achievement in bryophyte research and provides new insights for biodiversity conservation in the Shennongjia Nature Reserve. With the joint efforts of scientists and the public, we hope to better protect this rare species and promote bryophyte diversity research.(Written by Han Guoying)
Citation style: Huang, W.-Z., Tong, S.-G., & Zhu, R.-L. (2024). Dicranum shennongjiaense W.Z.Huang & R.L.Zhu (Dicranaceae, Bryophyta), a new species from Central China supported by morphological and molecular evidence. Journal of Bryology. Copyright Shennongjia National Park
Address:36 Chulin Road, Muyu Town, Shennongjia Forestry District, Hubei Province 鄂ICP备18005077号-3
Address:36 Chulin Road, Muyu Town, Shennongjia Forestry District, Hubei Province 鄂ICP备18005077号-3
Email:2673990569@qq.com
Phone:0719-3453368
Phone:0719-3453368


TOP

