Geological Time Scale
Updated:2021-10-12 Source:Shennongjia National Park
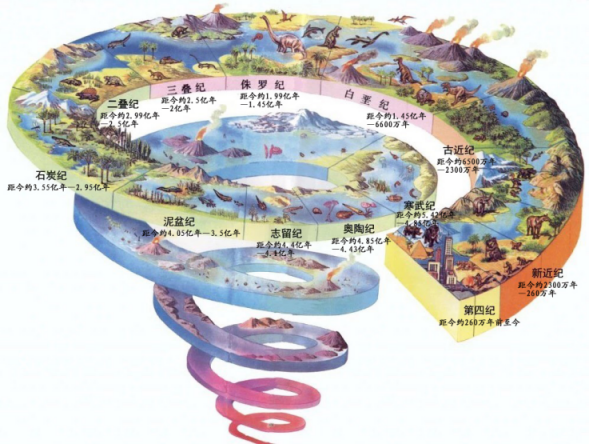
Spiral-shaped diagram for Geological Time and Biological Evolution
To carry out research into the evolutionary process of the Earth, geologists, based on the extant strata, paleobiological fossils, vestiges of crustal movements and in conjunction with data and information obtained from isotopic dating, have established the geological time scale.
The Earth has been known to be the only celestial body in the solar system where life exists, 71% proportion of the Earth’s surface is covered with ocean and 29% by land. The Earth is the home of human being, where ample resources are stored.
The Earth takes on a typical concentrically layered structure having internal and external circular layers. The solid portion of the Earth is composed of the crust, mantle and core from the surface to the central part, which are the three internal circular layers; whereas atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere on which mankind lives are the external circular layers on the Earth.
The Earth has been changing all the time during her long history for 4.6 billion years. The tremendously violent crustal movement may bring about continent-oceanic changes, forming lofty mountains, rivers and lakes, giving rise to mountain collapsing and earth cracking, volcanic eruption, earthquake, and tsunami.
Landforms are the products of both endogenetic and exogenetic processes in the Earth’s crust. With these two geological processes incessantly sculpting the Earth’s surface, various topographical and geomorphological landscapes are created.
The composition of materials forming the three circular layers varies. The major elements making up the core of the Earth are iron and nickel, the mantle is made up mainly of ferromagnesian silicate; the crust and the top part of the upper mantle are considered a world of minerals and rocks, which geologists term as lithosphere. Rocks are classified into three types in terms of their origins, namely, magmatic rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks.
The earth has a history of 4.6 billion years. How can we describe such a long timespan? By studying the evolution of the earth, geologists divided the age of the earth by different units, namely aeon, era, period and epoch according to the age of rock strata, and then made a geological time scale that directly reflects the evolution sequence of rocks, fauna and flora on grounds of chronologizing the geological history with each geological age unit, name and isotope age involved.
Address:36 Chulin Road, Muyu Town, Shennongjia Forestry District, Hubei Province 鄂ICP备18005077号-3
Phone:0719-3453368



