Main Types of Geological Heritage
Updated:2022-09-20 Source:Shennongjia National Park
Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark has various types of geological landscapes. According to the Guidelines for the Overall Planning of National Geoparks (2002) of the Ministry of Land and Resources of China (MLR), the Technical Requirements and Work Guidelines for the Construction of China's National Geoparks (Trial) (2000) prepared by the Department of Geological Environment of the MLR and the Technical Requirements for Planning and Compilation of National Geoparks of the MLR (2010) and other related planning standards, the geological relics in Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark are divided into 6 categories, i.e., typical geological sections, paleontological landscapes, geomorphologic landscapes, mountain landscapes, water landscapes, and geological disaster relic landscapes. Among the typical geological sections, stratigraphic units and stratigraphic boundary stratotype sections are the most abundant, while karst landforms and Quaternary glacial landforms are the most typical geological landscapes.
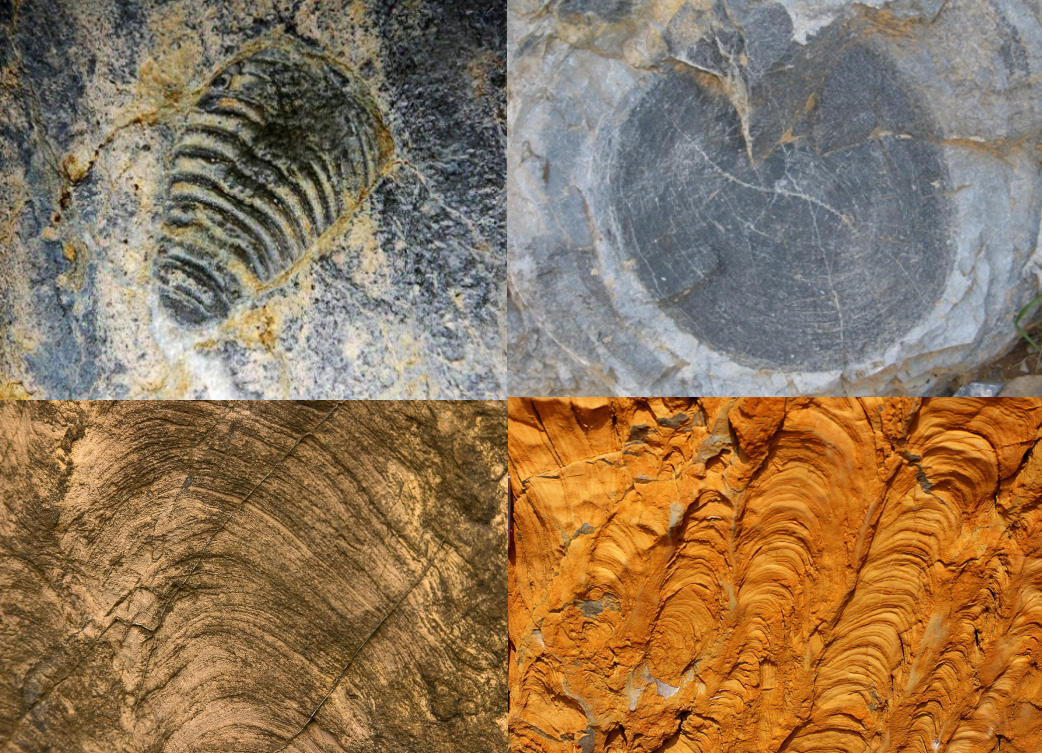
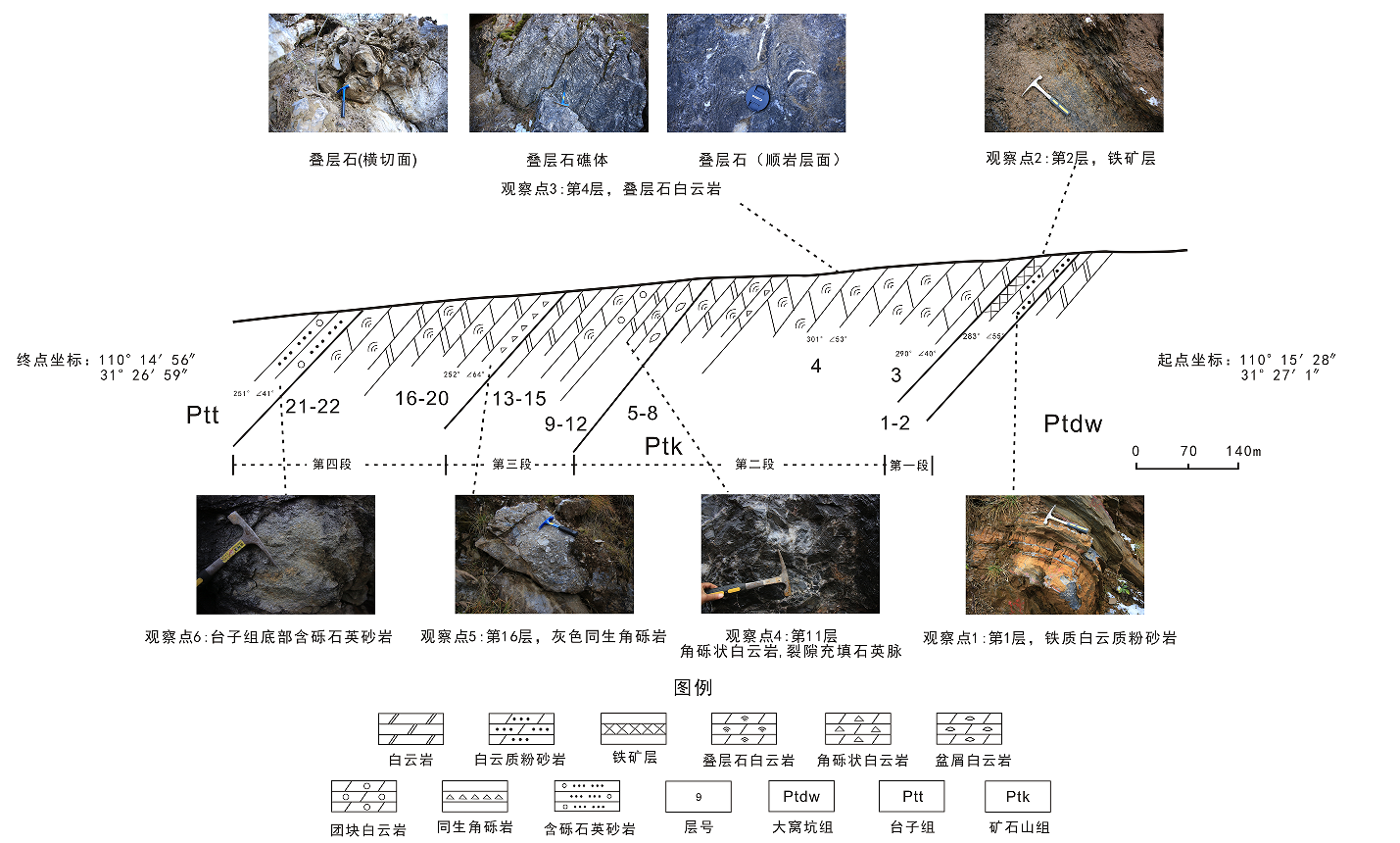





Paleontological landscapes
The paleontological landscapes feature abundant stromatolites in Late Precambrian strata. In the Shennong Valley section, since the Shicaohe Formation was formed in the initial formation stage of the carbonatite platform, the stromatolites in it are characterized by wavy, hemispherical, small cone and columnar shapes; Since the platform had entered a mature stage during the period of the Dawokeng Formation and the Kuangshan Formation, the stromatolites in them are mainly large cones and columns. Although the morphology and assemblage of stromatolites are mainly controlled by the sedimentary environment and hydrodynamic conditions, they are still an important basis for the sedimentary environment analysis and the stratigraphic division and correlation in the Proterozoic. The Cambrian strata are rich in trilobite and archaeocyatha fossils. The Ordovician strata are rich in echinoderms, brachiopods, trilobites, ostracods, gastropods, cephalopods and other fossils. The Silurian strata in Gangchangping are rich in graptolite fossils.
In 1995, the Pleistocene ancient human site (the ancient human Paleolithic site in Shennongjia) was discovered in the ancient rhinoceros cave at an altitude of 2,100m near Hongping. More than 1,000 paleontological fossils (such as rhino, giant panda and saber-toothed elephant fossils) and Paleolithic objects have been unearthed, which are of great significance to the study of the living environment, living range and adaptability of ancient humans.

Geomorphologic landscapes
There are many types of landforms in the park, which can be mainly divided into four categories, i.e., rock landforms, glacial landforms, fluvial landforms and tectonic landforms. These types of landforms constitute the picturesque natural scenery with lofty mountains, fantastic peaks and extraordinary valleys in Shennongjia.
Rock landforms
There are two main rock landforms in Shennongjia. One is carbonate karst landform, and the other is magmatic rock landform.
(1) Karst landforms
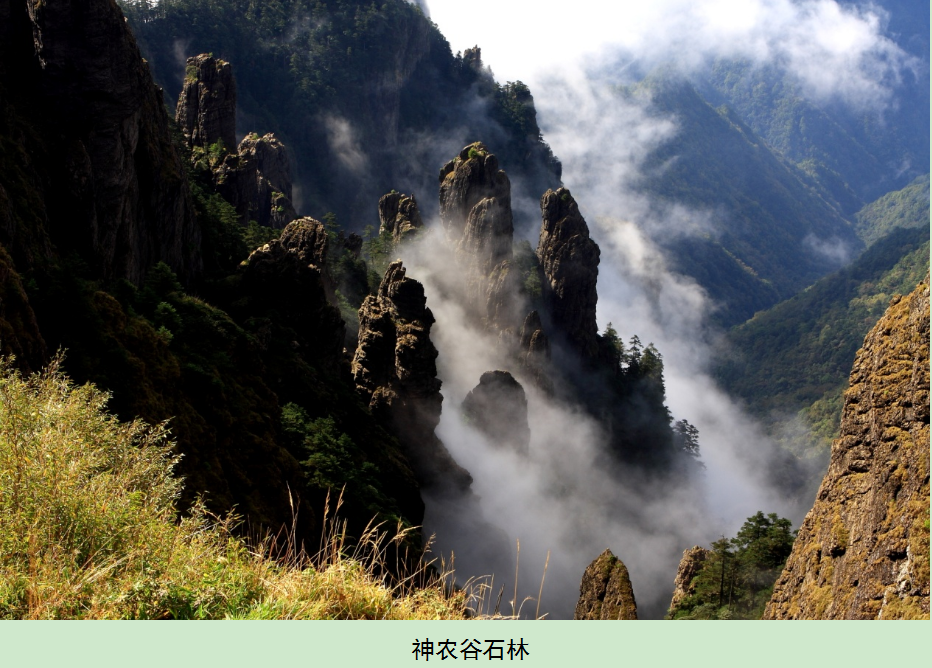
Soluble carbonate rocks are widely exposed in the park, which are mainly thick and super-thick dolostone of the Mesoproterozoic Shennongjia Group and some limestone and dolostone of the Neoproterozoic to the Ordovician. A series of karst depression, karst caves, underground rivers, basins, karrens, fluid bowls, clints, stone forests, trough valleys, dry valleys, karst peaks, natural bridges, etc. are formed under karstification. The Stone Forest in Shennong Vellay, Banbiyan Clint Forest, Dajiuhu Karst Basin, Houzishi Clint Forest and Nantianmen Stone Forest are particularly typical.
(2) Magmatic rock landforms
Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark has a basic magmatic dike swarm, which was formed in the Neoproterozoic period and was the product of the breakup of the Rodinia supercontinent. The basic dike is more resistant to weathering than the surrounding dolostone of the Mesoproterozoic Shennongjia Group. Therefore, after the surrounding carbonate rocks disappeared under karstification, the basic dike was preserved on the top of a series of peaks with an altitude of above 3,000m, such as the Shennong Peak, Jinhou Mountain and Laojun Mountain.

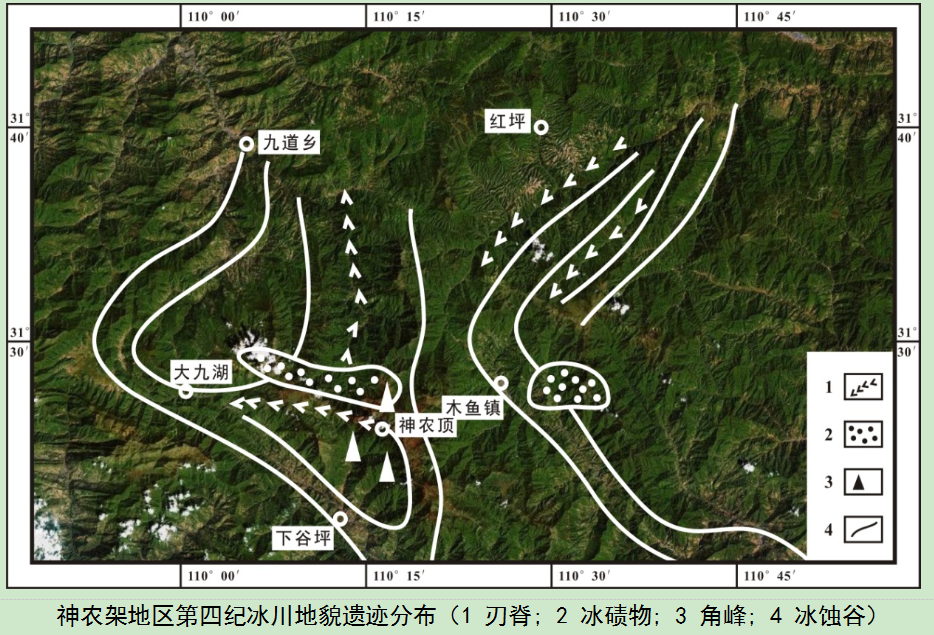
Quaternary glacial landforms
Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark is located in the mountainous area of western Hubei, on the eastern edge of the second step of China's topography. Under the action of Quaternary glaciers, a series of glacial landforms were formed, which can be divided into glacial erosional landforms, glacial depositional landforms and periglacial landforms.
(1) Glacial erosional landforms
Glacial erosional landforms mainly include cirques, horn peaks, edge ridges, and U-shaped valleys. Due to the high altitude of the main peak area of Shennongjia, which is composed of a series of peaks with an altitude of above 3,000m, there are various types of glacial landforms here. Glacial erosional landforms are clear, in which the glacier troughs and moraine-dammed lakes are best preserved. There are also well-developed cirques, horn peaks and edge ridges. These landforms are mainly seen in Dajiuhu, Shennongding, and Qingtianpao of Muyu Town.
(2) Glacial depositional landforms
Under the action of glaciers, a series of glacial depositional landforms developed at the bottom of glaciers, mainly including lateral moraine, bottom moraine and erratic. Among them, the Changyanwu glacial erratics and the Xiaojiuhu lateral moraine dam are the most typical.
(3) Periglacial landforms
In the late Pleistocene (1-40Ma), two periglacial periods developed in Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark, causing the formation of various periglacial landforms. The typical ones include the stone sea and debris flow deposit of the Shennong Peak, Hongshigou stone river, Chaoshuichi-Houzishi frost-weathered stone columns, and ice wedge and thawed curly structures of Songbai Town.

Fluvial landforms
Shennongjia belongs to the north subtropical monsoon climate zone, which is a transition zone from subtropical climate to temperate climate. Abundant precipitation has resulted in the development of numerous rivers in the park. Under the action of fluvial erosion and denudation, various fluvial landforms have been formed, which can be divided into fluvial erosional landforms and fluvial depositional landforms.
(1) Fluvial erosional landforms
In the Shennongjia area, the Mesoproterozoic Shennongjia Group thick and super-thick dolostone and the Neoproterozoic-Ordovician dolostone and limestone are well developed, which are prone to fluvial erosion. In addition, the park is rich in precipitation and rivers. In this context, a series of fluvial erosional landforms are formed. The typical ones include the Yinyuhe Canyon, the Shennong Valley, the Jinhou Waterfall, the Shuilian Waterfall, and the Gallery Valley of the Hongping Town.
(2) Fluvial depositional landforms
The Shennongjia area has many rivers, contributing to various fluvial depositional landforms in the lower reaches of the rivers and in the basins. Among them, the swamp peat deposition and the modern river profile of Dajiuhu are the most typical.

Tectonic landforms
Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark has experienced many tectonic movements, resulting in the formation of relatively unique tectonic landforms. There are mainly three types of tectonic landforms, i.e., planation surfaces, cliffs and folded mountains.
(1) Planation surface
Due to the intermittent uplift of the neotectonic movement in the area where the Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark is located, four levels of planation surfaces are formed in the mountainous area as follows:
1) The Shennongding period as the highest level of planation surface, with an altitude of 2,900-3,100m, is seen in the areas of Dashennongjia and Xiaoshennongjia, Shennong Peak, Houzishi and Laojun Mountain.
2) The Bawangzhai period, with an altitude of 2,500-2,700m, is distributed in the west and southwest, including Bawangzhai, Majiashan, Sifangtai, Dacaoping, Beifengping and other places.
3) The Exi period, with an altitude of 2,000-2,300m, is distributed in the north of Shennongjia, along the line of Songlang Mountain - Dayanwu with an altitude of 1,800-1,900m.
4) The Shanyuan period is the period when deep valleys, such as Yinyu River valley and Guanmen River valley, were formed in this area.
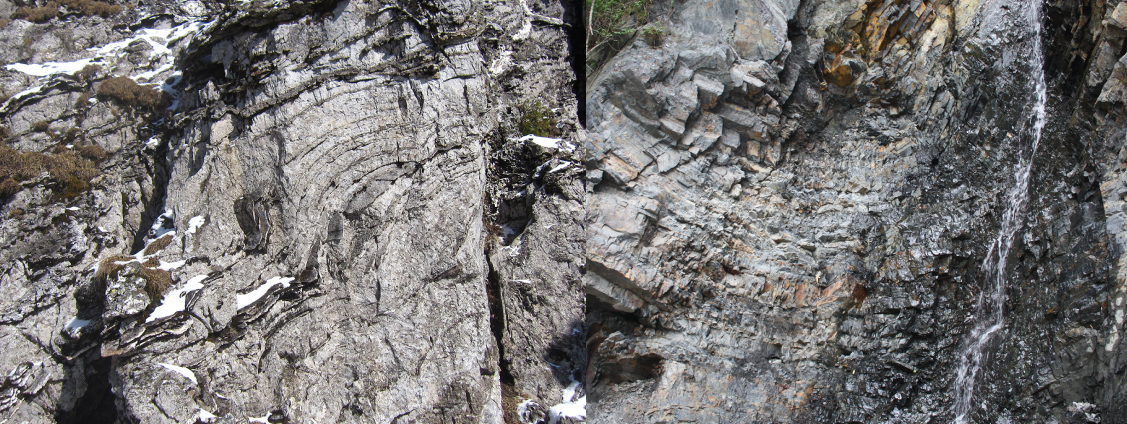
(2) Cliffs
A series of cliffs have been formed in the park under the action of fault structures, in which the most typical ones are Jiuchong cliff and Yanziya cliff.
(3) Folded mountains
The Shennongjia area is divided into the basement folds formed by the Mesoproterozoic strata and the later drape folds formed by the overlying strata. The main peaks and ridges of Shennongjia are composed of basement folds. For example, the peaks and ridges in the Shennong Valley-Liangfengya area are composed of a series of anticlines and synclines.

Water landscapes
(1) Rivers
Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark has high mountains and developed water systems. It is the watershed between the Yangtze River and the Hanjiang River in Hubei Province. With obvious characteristics of infancy, the river valleys in the park are steep and narrow, so the cross-section is mostly V-shaped. The large slope of the river valleys and the rapid water flow bring about abundant water energy resources. The development direction of the water systems in the park is controlled by the fault structures, while the density of the river network is controlled by the stratum lithology. In the clastic rock area, the river network density is generally above 1km/km2, with a maximum of 1.64km/km2. In the carbonate rock area, the river network density is generally 0.11-0.38km/km2. The rivers in the park mainly include the Longkou River, Changfang River, Dangyang River and Jiuchong River in the Xiangxi River system, which is a tributary of the Yangtze River; the Banqiao River, Huangxi River and Shizhu River in the Yandu River system, which is a tributary of the Yangtze River; the Guanmen River, Gushui River and Luoxi River of the Nanhe River System, which is a tributary of the Hanjiang River; and the Luoyang River, Yinyu River, Zizhu River and Pingdu River of the Guandu River System, which is a tributary of the Hanjiang River. The total surface water runoff of the park's rivers is 3,871.1 million m3/year. The Guandu River and Nanhe River, which are tributaries of the Hanjiang River, are the largest, followed by the Xiangxi River and Yandu River in the south, which are tributaries of the Yangtze River.
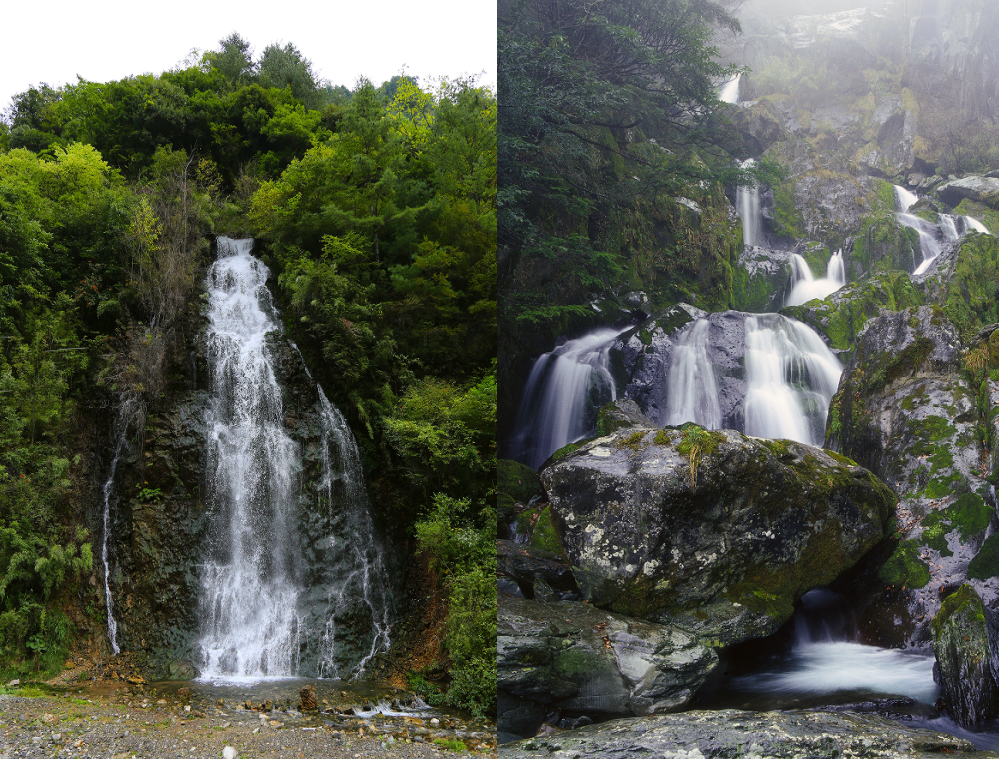
(2) Waterfalls
Due to the high and precipitous mountains, the large topographic relief, the development of steep walls and the abundant rainfall in the park, the water in the valleys flows through the hard rocks, often forming waterfalls. A typical waterfall is the Sanduihe Waterfall, Jinhou Waterfall, Tianshengqiao Waterfall, etc. The Jinhou Waterfall is particularly prominent with a height of about 30m and a width of about 5m, forming large water potential. In the dense virgin forest, the waterfalls flow down rapidly, forming a unique scene. The luxuriant ancient trees, the gorgeous waterfalls and the splendid mountains integrate to provide a picturesque scenery.
(3) Lakes
Among the lakes in Shennongjia, Dajiuhu Wetland is the most typical. Surrounded by mountains, the broad and open Dajiuhu lies in the largest alpine plain in central China. Due to abundant rainfall, aquatic plants are lush, covering 70% of the total area in the wetland. The peat layer is about 3-4m thick and the average thickness of the black soil layer is 120cm. Dajiuhu is a karst basin formed at the end of the Oligocene (25-40 million years ago). It once became a karst lake due to the blockage of groundwater channels. The lake water was dredged into a swamp, forming the current landscape, which is a typical representative of the subtropical mountain wetland swamp in China.
Geological disaster relic landscapes
The geological disaster relic landscapes in Shennongjia UNESCO Global Geopark are mainly mountain collapse relics, landslide relics and debris flow relics. The mountain collapse relics include the Sanduihe collapse, the Majiagou collapse of Xinglongsi village in Xiaguping Township, and the Banqiaohe rolling stones. The landslide relics include Xiaodangyang landslide, Shennong Sacrificial Altar landslide, Honghuaping landslide, Muyu Town landslide, and Sanduihe landslide; The debris flow relics include Xiaodangyang debris flow.
Copyright Shennongjia National Park
Address:36 Chulin Road, Muyu Town, Shennongjia Forestry District, Hubei Province 鄂ICP备18005077号-3
Address:36 Chulin Road, Muyu Town, Shennongjia Forestry District, Hubei Province 鄂ICP备18005077号-3
Email:2673990569@qq.com
Phone:0719-3453368
Phone:0719-3453368


TOP

