"Snowball Earth" Event and "Climate Warming" Event
Updated:2022-09-20 Source:Shennongjia National Park
The geological relics of Shennongjia have recorded many major geological events that have occurred over a billion years.
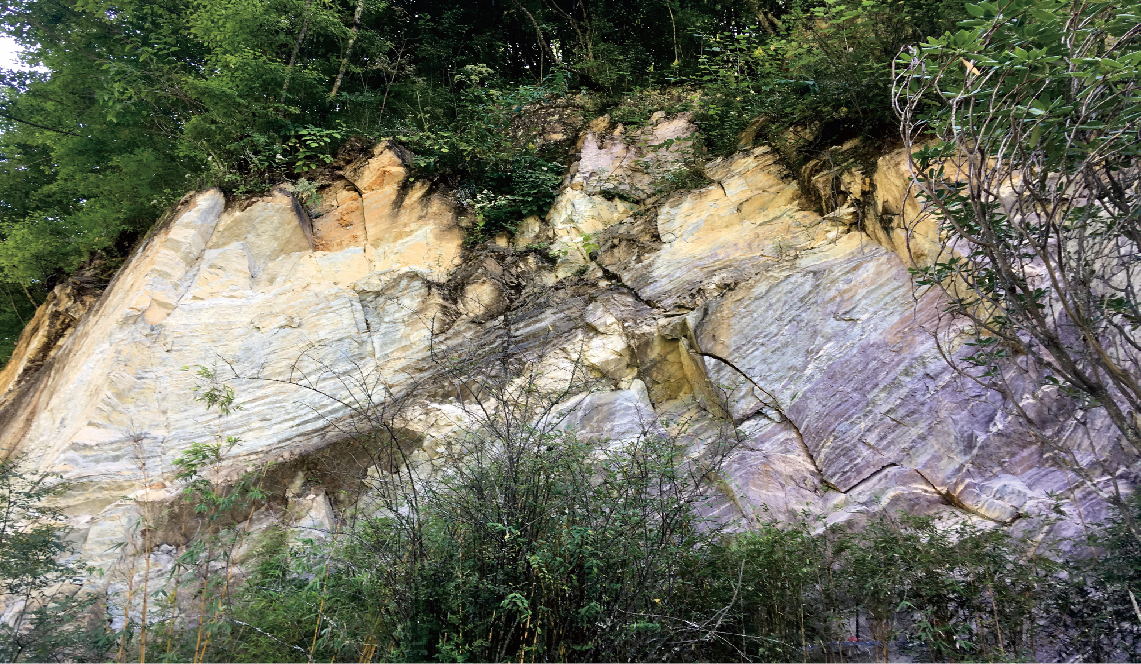
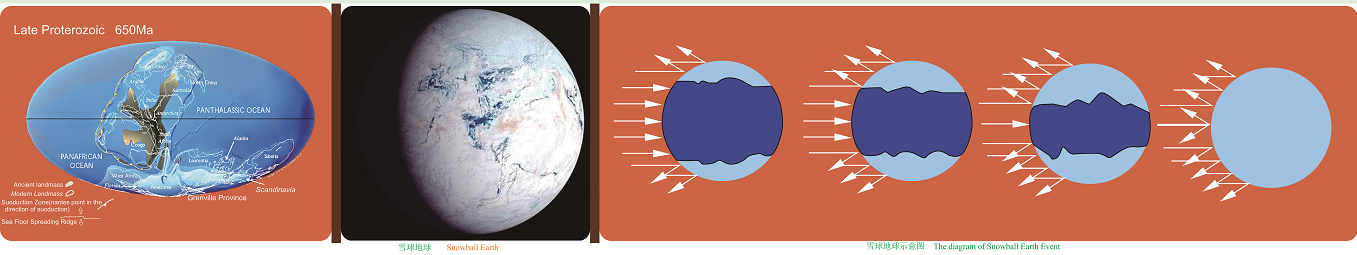

The moraine outcrop of the Nantuo Formation in Shennongjia is evidence of the "Snowball Earth" event more than 600-800 million years ago. At that time, the pangaea known as the "Rodinia supercontinent" broke up into many landmasses, so the total length of the coastline and the area of the marginal seas on the earth increased rapidly. The neritic environment on the continental margin is particularly conducive to the growth of plants like algae, while the plants consumes carbon dioxide in the atmosphere through photosynthesis and produces oxygen. As a result, the composition of the Earth's atmosphere was gradually changed. A sharp drop in carbon dioxide, which produces the "greenhouse effect", triggered an opposite climate change ("icehouse effect") on the Earth, which led to the continuous increase of ice and snow coverage on the Earth's surface. The ice and snow covered on the surface further enhanced the reflection of sunlight energy, resulting in the simultaneous enhancement of the "icehouse effect". In this context, the global temperature dropped sharply, and the Earth entered a very cold Ice Age. The whole Earth became a crystal ball covered with ice and snow from the poles to the equator.

It took quite a while for the frozen Earth to change in its deathly silence. When the magma at the bottom of the ground simmered to a certain stage, coupled with the tectonic movement of the plates, violent volcanic eruptions occurred. The magma poured out over an area of tens of thousands of square kilometers and a large amount of carbon dioxide and other gases were produced, which triggered the "greenhouse effect." The rapid increase in greenhouse effect led to a rapid rise in temperature near the equator. The whole earth gradually woke up from its slumber, and shifted from the coldest glacial period to the warm post-glacial period. This is the "climate warming" event in geological history.

Due to the warming of the global climate, weathering and sedimentation gradually intensified. As a result, the newly formed dolostone covered the glacial deposits of the Nantuo Formation. As a representative of a warm and dry climate, the dolostone overlay the glacial deposits, which is called "cap dolostone". In Shennongjia, the moraine stratum of the Nantuo Formation and the "cap dolostone" directly overlying it can be clearly observed. Since they are two rock formations reflecting diametrically opposite earth's climatic environment, such a stratigraphic distribution indicates that the Earth has undergone great changes.

Copyright Shennongjia National Park
Address:36 Chulin Road, Muyu Town, Shennongjia Forestry District, Hubei Province 鄂ICP备18005077号-3
Address:36 Chulin Road, Muyu Town, Shennongjia Forestry District, Hubei Province 鄂ICP备18005077号-3
Email:2673990569@qq.com
Phone:0719-3453368
Phone:0719-3453368


TOP

